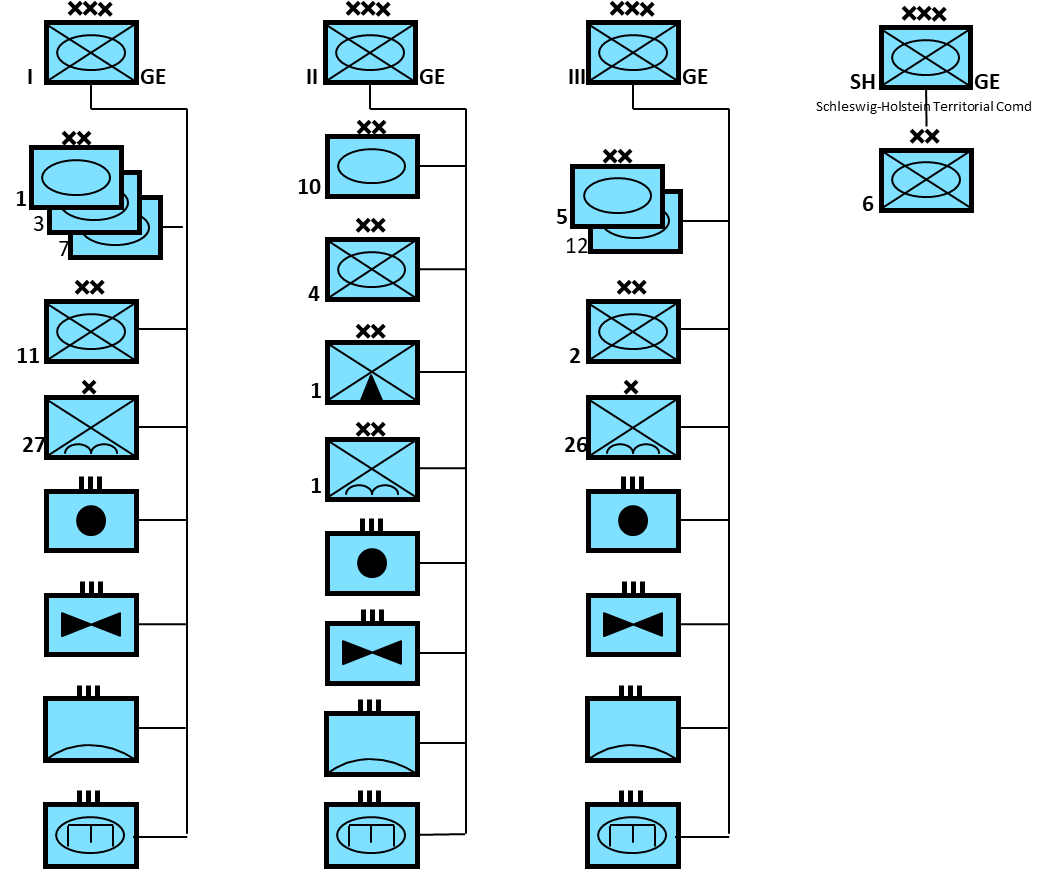
German Army (Deutsches Heer)
The current form of the German Army was founded on 12 November 1955, when West Germany joined the NATO alliance and reformed the military branch of government (Bundeswehr). By 1985 the army was at its established strength of 12 Divisions. The diagram below depicts the peacetime organizational structure. However, in wartime 3rd Panzer Division (I Corps) would transfer to the 1st Netherlands Corps, while 26 & 27 Fallschirmjäger Brigades would join 1st Fallschirmjäger Division and become SHAPE reserve.
The Schleswig-Holstein Territorial Command (SH) in wartime would take charge of several home defence Brigades and Regiments and operate as a Division or possibly Corps level HQ under Allied Command Baltic Approaches (BALTAP). 6th Panzergrenadier Division would also come under command BALTAP and, depending on the situation, operate independently or under the command of SH.
The pre-unification army had a strength of approximately 340,000 regulars and 717,000 reserves and territorial defence forces. The regular forces could deploy to their wartime (GDP – General Defence Plan) positions within 24 hours and full mobilization of reserves and territorials would happen within 3-4 days.
After unification the Heer merged with the Nationale Volksarmee of the former East Germany, forming the IV Corps headquartered in Potsdam, starting in 1990. Between 1990 and 1994 this fourth Corps was reduced in size until it was replaced in the Berlin/Potsdam area by III Corps. Very little former East German equipment was held, most of it was sold to finance unification. Since the bulk of both armies were conscripts, reduction of the total strength was simply a management issue. Historically, the structure and size of the Heer changed significantly between 1993 and 1996 – however these changes did not happen.
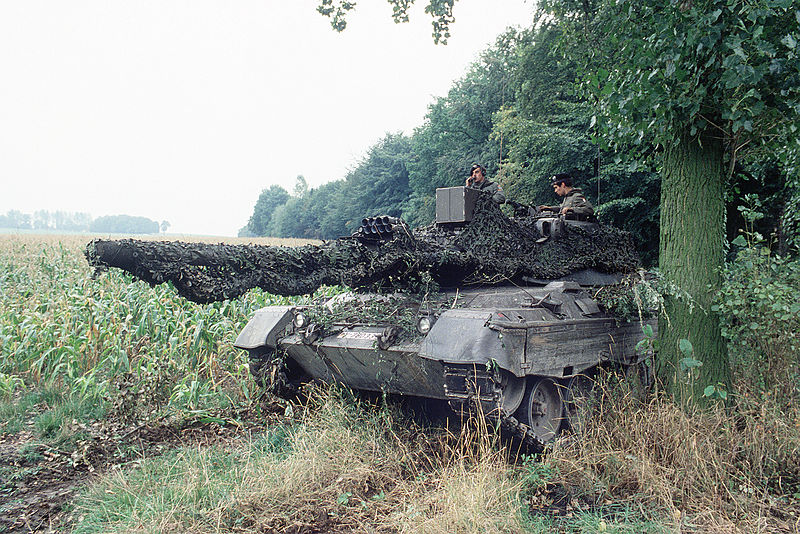
 Considered
by many to be the finest tank in the world with a 120mm L44 smoothbore
gun, a speed of 68 KPH, an operational range of 550Km with internal fuel
and excellent armor protection. This tank is at least on par with the
British Challenger 2, French Leclerc or the American Abrams M1A2. By
1994 the full production run of 2,125 was complete and retained by the
Heer. None of the engineering variants of the Leopard 2 had reached
production but the Armored recovery vehicle variant was starting to
arrive in units by 1994. Leopard I specialist variants were used
instead.
Considered
by many to be the finest tank in the world with a 120mm L44 smoothbore
gun, a speed of 68 KPH, an operational range of 550Km with internal fuel
and excellent armor protection. This tank is at least on par with the
British Challenger 2, French Leclerc or the American Abrams M1A2. By
1994 the full production run of 2,125 was complete and retained by the
Heer. None of the engineering variants of the Leopard 2 had reached
production but the Armored recovery vehicle variant was starting to
arrive in units by 1994. Leopard I specialist variants were used
instead.
 The
Leopard I was used widely throughout Europe and Canada as well. The
German Army operated a total of 2,437 of them. With the introduction of
the Leopard II, some were put into storage but most replaced M48s in
reserve units. 1,225 tanks were upgraded to the ultimate ‘A5’ standard,
while 250 were ‘A4’ versions, 110 were ‘A3’, 232 were ‘A2’ and the
remainder were upgraded to the improved Leopard 1 A1A1 standard. In
addition to the original production were large numbers of specialist
vehicles such as:
The
Leopard I was used widely throughout Europe and Canada as well. The
German Army operated a total of 2,437 of them. With the introduction of
the Leopard II, some were put into storage but most replaced M48s in
reserve units. 1,225 tanks were upgraded to the ultimate ‘A5’ standard,
while 250 were ‘A4’ versions, 110 were ‘A3’, 232 were ‘A2’ and the
remainder were upgraded to the improved Leopard 1 A1A1 standard. In
addition to the original production were large numbers of specialist
vehicles such as:
377x Gepard Anti-Aircraft variants.
105x Biber Bridge Layers.
444x Bergepanzer 2 Armored Recovery Vehicles (ARV).
36x Bergepanzer 2A1 ARV for engineer vehicles.
140x Badger Engineering vehicles.
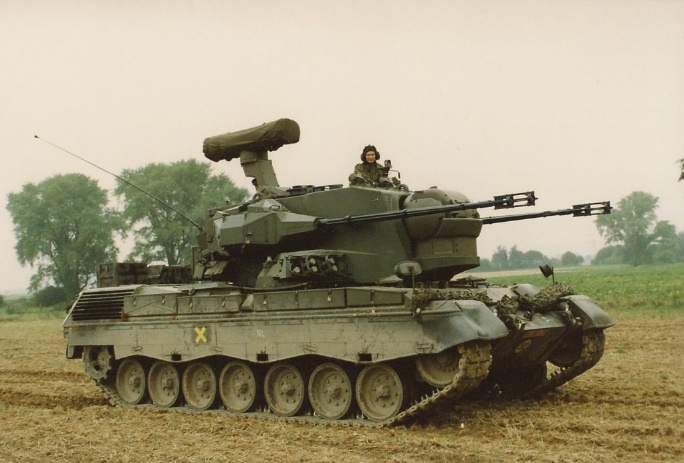

Gepard
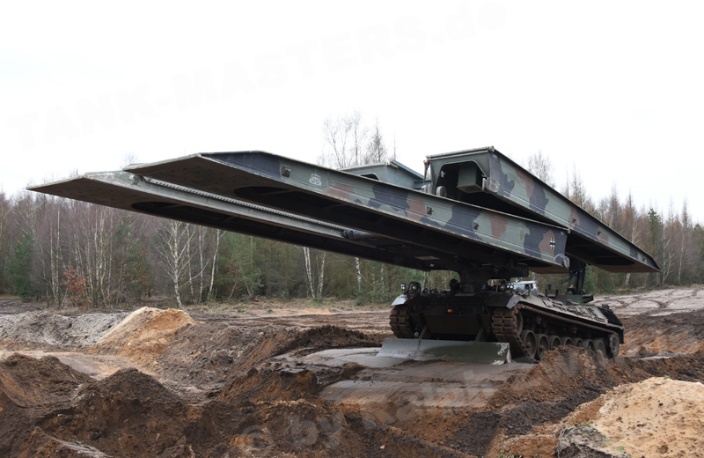

Biber Bridge Layer

Bergepanzer ARV
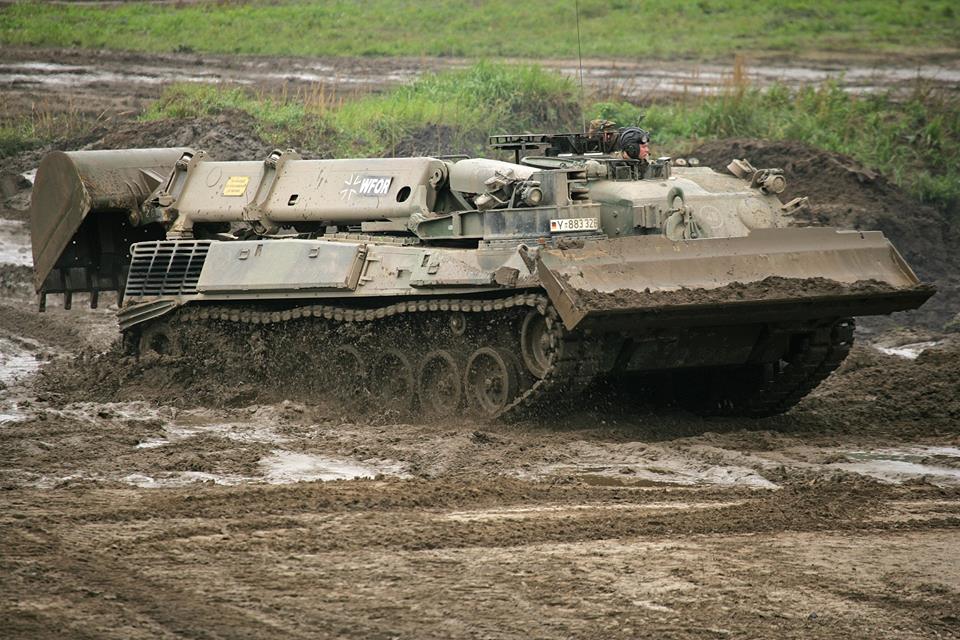

Badger
Luchs Armored Reconnaissance Vehicle

The German Army used 408 of these 8-wheeled amphibious vehicles in their reconnaissance battalions. With 8-wheel drive and all wheel steering, being equipped with thermal sites, a 20mm cannon and long-range radios, it was ideal for the job it was tasked for. It had two driving positions, one at each end of the vehicle for rapid reverse.

Germany was the first NATO country to adopt the IFV (Infantry Fighting Vehicle) concept with the Marder, with 2,133 of these vehicles used in Panzergrenadiere units. In addition to the 20mm Cannon and the Milan ATGM (Anti Tank Guided Missile), the soldiers in the passenger compartment can engage targets from inside the vehicle or quickly dismount and assault. The Marder can carry 12 infantrymen but normally carried a crew of 3 with 7 dismountable soldiers as passengers.
M113 Family
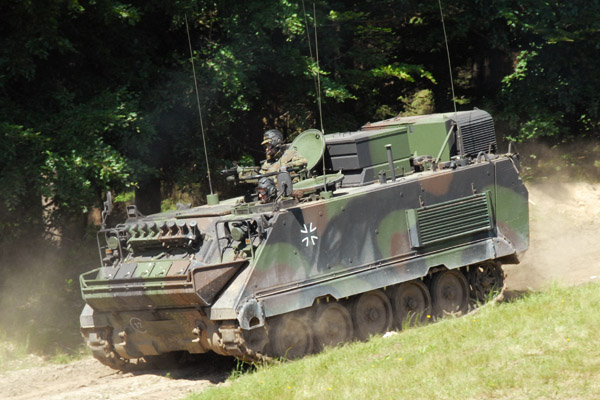

More than 4,000 of the ubiquitous M113 were in use. In addition to thousands used as infantry carriers’ numerous variants are found in the German Army, including:
+220x M577 Command Post.
+500x Panzermorser 120 – 120mm Self Propelled Mortar.
154x Artillery Fire Control variants.
320x Beobachtungs Panzer Artillery observation vehicles.
301x M548G Skorpion Minenwerfer, mobile mine dispenser.
Forward Air Controller variant.
Electronic Direction-Finding variant.
Signals vehicle.
Ambulances.
Radar carriers.
Artillery locating Radar carrier.

The Fuchs is a Six-wheeled Armored Personnel Carrier (APC). The German Heer operated 1,040 of these vehicles in several variants. The basic vehicle was amphibious and designed to carry a crew of 2 with 10 passengers. Variants include:
550x Standard Fuchs 1.
87x Non amphibious versions with larger payload.
265x fitted with various mission kits.
140x NBC reconnaissance vehicles.
Tank Destroyers
Three types of tank destroyers were used by the German Army. The idea was that these had the firepower of a tank but neither the maneuverability nor the protection. By 1994 the firepower was also less impressive.
607x Kanonenjagdpanzer, with a 90mm gun.
316x Jaguar 1, a similar chassis with a HOT ATGM.
162x Jaguar 2, a Kanonenjagdpanzer with the gun replaced by a TOW2 ATGM

Kanonenjagdpanzer

Jaguar 1
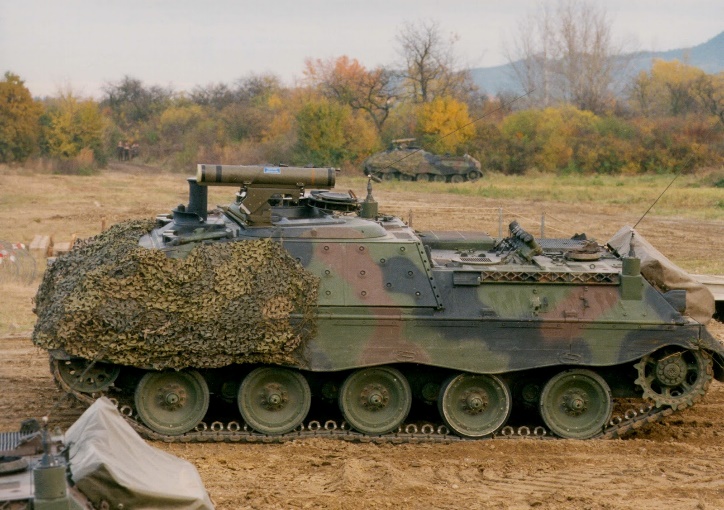

Jaguar 2